Inertial Case studies
Inertial Case studies

Clinical Success with the 3DMA System: Biomechanical Gait Analysis in Action
In the world of clinical biomechanics, having advanced tools for movement assessment is essential to improve patient diagnosis and treatment. FREMAP Majadahonda and FREMAP Sevilla hospitals have been using 3DMA from STT Systems as their primary solution for gait analysis and biomechanical evaluation for years, achieving outstanding results tailored to their needs. Additionally, a prestigious […]
Read more »
Duke University and the Use of ISEN in Clinical Research
Innovation in Biomechanical Analysis for Neurological Disorders In the world of clinical research, precision in movement measurement is crucial for developing new diagnoses and treatments. The Duke University School of Medicine has successfully integrated the ISEN solution from STT Systems into its clinical research laboratory since 2022, revolutionizing the way they evaluate patients with neurological […]
Read more »
How NamSeoul University Uses Motion Capture in Biomechanics Education
Motion capture is a key tool in teaching biomechanics and physical therapy. For over six years, NamSeoul University has relied on iSen by STT Systems as part of its educational methodology in the Department of Physical Therapy, using it for gait analysis and human movement biomechanics. According to Dr. SangBin Lee, PT, PhD, professor at […]
Read more »
iSen for Gait Analysis
The Utility of Inertial Sensors in Gait Analysis Inertial sensors are an increasingly popular tool in the analysis of human gait. These devices measure the acceleration and angular velocity of moving body parts and can provide valuable information about the way we walk. The use of inertial sensors in gait analysis has many advantages. For […]
Read more »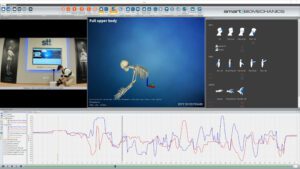
Analyzing the Ergonomics of Workstations using Inertial Sensors (IMUs)
Ensuring that a workstation is ergonomically designed is critical for maintaining the health and safety of workers. One way to evaluate the ergonomic design of a workstation is through the use of inertial sensors and biomechanical analysis. These tools provide objective data that can be used to identify potential risks and make adjustments to improve […]
Read more »
Biomechanical Analysis of Swimming Using Inertial Sensors
Swimming is an excellent exercise that engages all major muscle groups and is considered low-impact, making it a popular choice for people of all ages and abilities. However, to optimize performance and prevent injury, it is essential to understand the biomechanics of swimming. Biomechanical analysis of swimming can be performed using inertial sensors, which are […]
Read more »
Ice hockey analysis with iSen
Biomechanical hockey analysis with inertial sensors (IMUs) Hockey is a fast and physical sport that requires specific technical and physical skills. To improve player performance and prevent injuries, it’s important to understand how athletes move and act on the field. This is where biomechanical analysis comes into play. Biomechanical analysis uses sensor technology to measure […]
Read more »
iSen and inertial sensors arrive at Gimbernat University Schools
The School of Physiotherapy of the Gimbernat University Schools, on the Torrelavega campus, has begun to use its new STT-IWS inertial sensors and the iSen system. The iSen system uses STT-IWS inertial sensors that provide real-time angles as well as angular velocities and accelerations. They communicate wirelessly via Wi-Fi, so they can transfer information to […]
Read more »